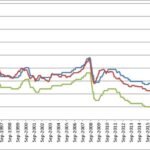
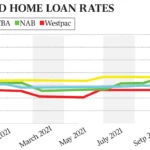
Home loan rates in New Zealand vary depending on factors like the type of loan, the bank or lender you choose, the length of the loan term, and your personal financial situation. Understanding how home loan rates work is crucial when buying a home, refinancing, or looking to switch lenders for better rates. Below, we’ll provide an overview of the different types of home loans, current market trends, and how you can secure the best home loan rates.
1. Current Home Loan Rates in New Zealand
Home loan rates in New Zealand typically fall into two categories: fixed-rate and variable-rate. Each option has its own set of advantages and considerations, depending on the borrower’s needs.
Fixed-Rate Home Loans
A fixed-rate home loan locks in an interest rate for a set period, usually between 6 months and 5 years. This offers the advantage of predictable monthly repayments, regardless of any interest rate changes during that period.
| Loan Type | 1-Year Fixed Rate | 2-Year Fixed Rate | 3-Year Fixed Rate | 5-Year Fixed Rate | Variable Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Home Loan Rate | 6.25% | 6.45% | 6.55% | 6.75% | 6.10% |
These rates are indicative and may vary based on the applicant’s financial profile and the lender’s current offerings. Rates tend to fluctuate due to changes in the market and the Official Cash Rate (OCR) set by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand.
2. Types of Home Loans Available
Different home loan products are designed to meet various borrower needs. Here’s an overview of the main home loan types available in New Zealand.
1. Fixed-Rate Home Loans
A fixed-rate loan offers interest rates that remain the same for a set period. This ensures predictable repayments, making it ideal for borrowers who want financial stability and certainty in their mortgage payments.
Advantages:
- Fixed monthly payments regardless of market fluctuations.
- Predictable budgeting for the loan term.
Disadvantages:
- Typically higher rates than variable loans.
- Limited flexibility to take advantage of falling interest rates.
- Break fees for early repayment of fixed-rate loans.
2. Variable-Rate Home Loans
A variable-rate home loan means the interest rate can change over time. These loans are directly influenced by market conditions, and rates may increase or decrease based on changes to the Official Cash Rate (OCR).
Advantages:
- Flexible repayment options without penalties.
- Rates may decrease if the Reserve Bank cuts the OCR.
- No early repayment penalties.
Disadvantages:
- Payments may fluctuate, making it harder to budget.
- Potential for rate hikes if the OCR increases.
3. Split Loans
A split home loan is a combination of both fixed and variable rates. For example, you could have a portion of your loan on a fixed rate for security, while the other portion is variable for flexibility.
Advantages:
- Combines the security of fixed rates with the flexibility of variable rates.
- Helps manage the risks of fluctuating interest rates.
Disadvantages:
- More complex to manage.
- May not offer the full benefits of either fixed or variable rates if not balanced correctly.
3. Factors That Influence Home Loan Rates
Several factors affect the interest rates on home loans in New Zealand. These factors can help determine the rates you will be offered by lenders like banks and other financial institutions.
1. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand’s OCR
The Official Cash Rate (OCR) is one of the most significant influences on home loan rates in New Zealand. The OCR is set by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand and determines the interest rate at which banks borrow money. When the OCR rises, banks usually raise their lending rates, and when the OCR falls, borrowing costs decrease.
2. Loan-to-Value Ratio (LVR)
The Loan-to-Value Ratio (LVR) refers to the proportion of the property value that you borrow. A higher LVR typically means higher interest rates because the lender perceives more risk in lending you a higher percentage of the property value. Generally, loans with an LVR of 80% or less are considered lower risk and may attract better rates.
3. Your Credit Score
Lenders assess your credit score when deciding the interest rate to offer. A higher credit score reflects good financial behavior and a lower risk to lenders, which can result in a more favorable rate. A low credit score, on the other hand, can lead to higher rates or rejection of the application.
4. The Length of the Loan Term
Longer loan terms, such as 30 years, generally come with higher interest rates because the lender faces a longer period of risk. Shorter loan terms (such as 15 years) typically come with lower rates but higher monthly repayments.
5. Economic and Market Conditions
Interest rates also reflect broader economic conditions. Factors like inflation, economic growth, and global financial markets can impact how much it costs for banks to lend money, which, in turn, affects home loan rates.
4. How to Secure the Best Home Loan Rates
To get the best possible deal on your home loan, consider the following tips:
1. Improve Your Credit Score
A strong credit score is key to securing a low interest rate. Pay off existing debts, avoid late payments, and monitor your credit report regularly to ensure accuracy.
2. Save for a Larger Deposit
The larger your deposit, the lower your Loan-to-Value Ratio (LVR). This reduces the risk for lenders and can help you secure a better rate. A deposit of 20% or more is often ideal to avoid paying Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI).
3. Shop Around and Compare Lenders
Don’t settle for the first offer. Take time to compare home loan rates and features from different lenders to find the best deal. Online comparison tools can make this process easier.
4. Consider Loan Term and Structure
The term of your loan can significantly affect your interest rate. If possible, choose a shorter term for lower rates. Alternatively, a split loan may give you a balance of fixed and variable rates for flexibility.
5. Look for Special Deals and Discounts
Many lenders, including the big banks in New Zealand, offer special deals or discounts for new customers, first-time homebuyers, or those looking to refinance. Keep an eye out for such offers to secure a competitive rate.
5. Home Loan Fees and Costs to Consider
While interest rates are a major factor, it’s also important to consider the fees and other costs associated with a home loan. Common fees may include:
- Application Fees: Some lenders charge fees for processing your home loan application.
- Valuation Fees: If the bank needs to assess the value of the property, they may charge a valuation fee.
- Legal Fees: Costs related to the legal processing of the loan.
- Early Repayment Fees: If you repay your loan early, especially for a fixed-rate loan, you may face a penalty.
- Monthly Service Fees: Some banks charge a monthly fee to maintain your loan.
Make sure to factor these additional costs into your decision to get a clear picture of your total loan expenses.
6. How to Apply for a Home Loan in New Zealand
The process of applying for a home loan in New Zealand generally involves the following steps:
1. Determine Your Borrowing Capacity
Use an online home loan calculator to determine how much you can borrow based on your income, expenses, and the size of your deposit.
2. Gather Required Documents
Lenders typically require proof of identity, income, and details about the property you wish to purchase.
3. Submit Your Application
Once you’ve chosen a lender and loan type, submit your application. The lender will assess your financial situation and creditworthiness.
4. Loan Approval and Settlement
After approval, you’ll receive your loan offer. If you accept the terms, you can move forward with the settlement process, which involves signing the loan agreement and transferring the property ownership.
In New Zealand, home loan rates are an essential factor to consider when purchasing a property. By understanding the different types of loans, factors influencing rates, and how to secure the best possible deal, you can make an informed decision that suits your financial situation.